MRI is a radiology technique in which images of body structures are made with the help of magnets, radiowaves and computers. MRI is based on the principle of NMR (Nuclear magnetic resonance). The first man's MRI SCAN was done in 1977. At that time an MRI image used to come in 5 hours.
RAYMOND VAHAN DAMADIAN is called FATHER OF MRI. He first introduced the idea of a large NMR scanner for the detection of malignant tissue in 1972. Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield invented the MRI machine in 1973.
Principle of MRI
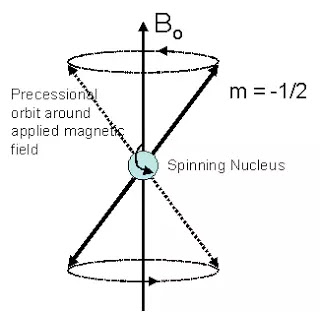
Some atomic nuclei have magnetic properties. These atomic properties are due to the rotation of the nucleus of those atoms on their own axis and also the precessional rotation of their axis. MRI uses these magnetic properties of these atoms. Hydrogen atom has only one proton.
This atom is found in water. Therefore, it is also found in abundance in your body, because there is 70% water in your body.
This hydrogen atom keeps spin movements around its axis. This movement is random. By using an external strong magnetic field, these hydrogen nuclei can be aligned in only one direction. When radio waves are inserted on these aligned nuclei, they start doing precessional rotations while returning to equilibrium.
And also emit a radio signal. This radio signal is detected by antenna coils. Through this signal, a high detailed image of soft tissue is obtained from the computer process.