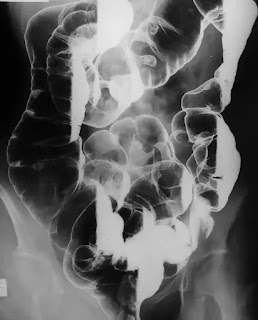
barium enema in radiology
Method
- The ten day rule is followed in female.
- Single contrast - Uses
Single contrast method is used to reduce intussusception.
There are lots of regimes of bowel preparation present. Suggested regimes-
Picolax tablet should be given at 08: 00h and 18: 00h.
Antibiotic prophylaxis should be given to those patients who have a prosthetic heart valve or who have a history of endocarditis.
- Double contrast - Mucosal pattern is observed.
Indication
- Change in bowel habit
- Pain
- Mass
- Melaena / anaemia
- Obstruction
Contraindication
Absolute
- Toxic megacolon
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Rectal biopsy via:
b. Barium enema is not done if endoscopy is done 24 hours before a flexible endoscope.
Relative
- Incomplete bowel preparation.
- Recent barium meal.
Contrast medium
- Polibar 115% w / v 500 ml or more.
- Air
Patient preparation
- 3 days before examination-
- The day before the exam -
Picolax tablet should be given at 08: 00h and 18: 00h.
- Exam day
Antibiotic prophylaxis should be given to those patients who have a prosthetic heart valve or who have a history of endocarditis.Preliminary film
Preliminary plain abdominal film is not required unless-
- Patient has severe constipation, which makes bowel preparation doubtful.
- Toxic megacolon suspected to be
Technique
- After heating the patient on one side of it, gently place the catheter in his rectum and connect it to the barium bottle and hand for air injection.
- After this barium starts pouring in as well as intermittent screening of barium continues and as barium reaches hepatic flexure and stops barium infusion.
- Now slowly pump the air into the bowel so that the barium column moves towards the caecum and produces double contrast effect. Some centers use Co2 gas for a double contrast effect, which reduces the post double contrast enema pan.
- Roll the patient on its left side and bring it to the RAO position so that the bowel mocosa will coat well.
Films
- Spot film for rectum and sigmoid colon -
- RAO
- Prone
- LPO
- Left lateral of the rectum.
- LAO to open out the splenic flexure
- RAO to open out the hepatic flexure
- Right lateral of the rectum
- Let the patient sleep on the supine right side in the head down tilt position and take the film. At this stage, the double contrast effect occurs in the caecum.
- Supine
- Prone
- Left lateral decubitus
- Right lateral decubitus
- Prone with tube angled 45 ° cauded and centered 5 cm above the posterior superior iliac spine.
Aftercare
- The patient should be told that due to barium, his bowel motions will be white for a few days and there may be problems in flushing.
- The patient should be advised to drink sufficient amount of water to prevent barium from freezing. Laxatives can be taken if required.
Complication
- Perforation of bowel
- Transient bacteraemia.
- Changes in partial large bowel obstruction of patient due to the deposition of barium into complete large bowel obstruction.