CELL CYCLE & CELL DIVISION
Introduction
cell division सभी सजीवों के लिए एक critical process है। एक cell division के दौरान कई process होती हैं। जैसे-DNA प्रतिकृति तथा cell growth आदि ।
घटनाओं का यह क्रम जिसमें cell अपने genome का doubling व divided होकर दो नई progeny cell का निर्माण करती है, इसे cell cycle कहते है।
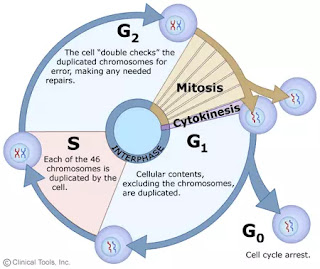
Stages of cell cycle :-
cell cycle की दो key stages होती हैं -
1. Interphase 2. Cell division
1. Interphase :-
interphage को Pause stage भी कहते हैं, क्योंकि इस stage में cell division के लिए तैयार होती है। यह अन्त्यावस्था (Telophase) के समाप्त होने तथा पूर्वावस्था (Prophase) की बीच की stage है।
interphage को three stages में divided किया गया है।
(A) G1 phase (B) S phase (C) G2 phase
(A) G1 phase:- इस phase में RNA तथा protein संश्लेषण होता है। इसमें interphage का 30-40% time लगता है।
(B) S phase:- इस अवस्था में RNA तथा protein का संश्लेषण होने से DNA के cords की संख्या double हो जाती है। इसमें interphage का 30-50% time लगता है।
(C) G2 phase:- इस अवस्था में DNA की मात्रा somatic cells की तुलना में दुगुनी हो जाती है और cell Mitosis के लिए तैयार हो जाती है।
2. Cell division :-
cell division के समय पहले nucleus का division होता है तत्पश्चात् cytoplasm का division होता है। cell division मुख्य रूप से two type से होता है-
(i) Mitosis
(ii) Meiosis
(i) Mitosis :-
सर्वप्रथम W.Fleming ने mitosis को बताया।
Importance:- इस प्रकार के mitosis में main Parent cell दो Daughter cells में परिवर्तित हो जाती है। इस प्रकार के cell division में chromosomes की संख्या में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं आता है। यह division somatic cells में होता है। इसे अप्रत्यक्ष विभाजन(indirect division) भी कहते है।
Stages:- mitosis की different stages निम्न प्रकार से हैं-
(A) Prophase (B) Metaphase (C) Anaphase (D) Telophase
(A) Prophase :- इस stage में chromosomes पतले परन्तु कुंडलित होकर छोटे व स्पष्ट होने लगते हैं।
प्रत्येक chromosome एक-दूसरे पर लिपटे रहते हैं, इसे chromatid कहते हैं। chromatid centromere से चिपकते हैं। chromosomes पर chromomere granules तथा चारों ओर Matrix एकत्रित होने लगता है।
अन्त में nuclear membrane तथा centripetal invisible हो जाते हैं।
(B) Metaphase :- इस stage में arguments(तर्कुओं) का निर्माण होता है -
chromosome मध्यरेखा पर एकत्रित हो जाते है, centromere दो भागों में बंट जाते हैं।
तथा centromere मध्यरेखा की ओर व chromosome की भुजाएँ ध्रुवों की ओर होती हैं।
(C) Anaphase :- यह mitosis की सबसे छोटी stage है। इस अवस्था में chromatid पृथक होना प्रारम्भ कर U, V या L आकार में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं। chromosome दो विपरीत ध्रुवों की तरफ जाने लगते हैं।
(D) Telophase :- इस stage में chromosome विपरीत ध्रुवों पर एकत्रित हो जाते हैं। chromosomes के चारों ओर nuclear membrane का निर्माण हो जाता है। centripetal, nuclear membrane का निर्माण हो जाता है, अतः सम्पूर्ण प्रक्रिया में एक cell से दो daughter cell बन जाती हैं।
cytoplasmic division :- cell nuclear division पूर्ण होने पर अंत में cell स्वयं एक अलग प्रक्रिया द्वारा दो progeny cells में divided हो जाती है। इसे cytoplasmic division कहते है।
(ii) Meiosis :-
Scientist Farmer & Moore ने meiosis नाम दिया। इस division से cell का nucleus दो बार divided होता है।
importance :- meiosis germ cells में होता है। इस division में daughter germ cells में chromosomes की संख्या घटकर half हो जाती है। इस division को direct division भी कहते हैं।
Stages of Meiosis :- meiosis को दो चरणों में विभक्त किया है -
(A) Meiosis I
(B) Meiosis II
(A) Meiosis I :- इसे निम्नांकित stages में विभाजित किया गया है -
(i) Prophase :- यह stage लम्बी तथा जटिल प्रावस्था है, जो निम्न है -
(a) Leptotene :- chromosomes लम्बे तथा पतले होते हैं, जिनमें से half chromosomes मातृक(maternal) तथा half पैतृक(ancestral) होते हैं।
(b) Zygotene :- इस stage में दो समान गुणसूत्र(identical chromosomes) युग्मन(coupling) कर सूत्रयुग्मन(conjugation) बनाते हैं, जिससे प्रत्येक pair में चार half chromosome दिखते हैं।
(C) Pachytene :- इसमें chromosomes कुण्डलित होकर छोटे हो जाते हैं। समजात chromosomes में Exchange होता है। समजात chromosomes चार half chromosomes , जिसे quaternary कहते हैं, का निर्माण
करते हैं।
(d ) Diptotene :-इस stage में समजात chromosomes में प्रतिकर्षण होने लगता है। परिणामस्वरूप पृथक होकर कायज्मेटा (Chiasmata) का निर्माण करते हैं। chromosomes की लम्बाई में कमी आने लगती है। साथ ही centripetal invisible हो जाती है।
(e) Diakinesis :- chromosomes संकुचित होकर गोल दिखाई देने लगता है। nuclear membrane तथा centripetal invisible हो जाती है।
(ii) Metaphase :- इस stage में chromosomes मध्यरेखीय क्षेत्र में एकत्रित होते है तथा centromere तन्तु से जुड़ जाते है।
(iii) Anaphase I :- इस stage में chromosomes मध्यरेखीय क्षेत्र से विपरीत ध्रुवों की ओर चले जाते हैं, centromere divided होकर एक-एक रह जाता है। प्रत्येक chromosomes आधे होकर ध्रुव पर पहुँच जाते हैं। (iv) Telophase I :- इस stage में nucleus cover व centripetal पुनः clear दिखाई देने लगते है साथ ही cytoplasmic division प्रारम्भ हो जाता है।
(B) Meiosis II :- यह division mitosis के समान होता है। इस division में chromosomes की संख्या में कोई भी परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। इसकी निम्नांकित चार stages हैं -
(i) Prophase II :- इस stage में nucleus तथा nuclear membrane invisible हो जाती है। chromosomes पर मेट्रिक्स स्पष्ट होती है।
(ii) Metaphase II :- इस stage में arguments का निर्माण होता है। समस्त chromosomes मध्यांश पर एकत्रित हो जाते हैं। प्रत्येक chromosomes के दो half-chromosomes, centromere स्थल पर एक-दूसरे से पृथक हो जाते हैं।
(iii) Anaphase II :- इस stage में centromere अलग होकर अर्धगुणसूत्र विपरीत ध्रुवों की ओर चले जाते हैं। (iv) Telophase II :- यह stage meiosis की अन्तिम stage है। इसमें half-chromosome विपरीत ध्रुवों पर एकत्रित हो जाते हैं तथा अन्त में nucleus, centripetal तथा centripetal art का निर्माण होता है। इन stages के पश्चात् पुनः cytoplasm का division होकर अगुणित chromosome वाली चार daughter cells का निर्माण होता है।
CHARACTERISTICS OF CELL
समस्त जीवधारियों के लिए cell एक Basic रचनात्मक एवं क्रियात्मक इकाई है, जिसकी निम्नलिखित विशेषताएँ हैं -
1. Respiration
जीवधारियों को जीवित रहने के लिए oxygen की आवश्यकता होती है, यह आवश्यकता respiration द्वारा पूर्ण होती है। respiration क्रिया का अर्थ oxygen ग्रहण करना तथा कार्बन-डाई-ऑक्साइड बाहर निकालना है। अतः respiration क्रिया कोशिका का विशिष्ट गुण है।
2. Growth & Repair
cell शरीर के लिए growth तथा repair का महत्वपूर्ण कार्य करती है। growth क्रिया nutrients के assimilation के फलस्वरूप उत्पन्न होती है साथ ही repair cell का विशिष्ट गुण है जो cell के cytoplasm द्वारा पूर्ण होता है।
3. Assimilation
शरीर की प्रत्येक cells assimilation की क्रिया करती है अर्थात् cells द्वारा nutrients को ग्रहण किया जाता है जिनका Intestines की wall द्वारा absorption होता है तत्पश्चात oxidation की क्रिया पूर्ण होती है जिसके फलस्वरूप energy या power उत्पन्न होती है।
4. Irritability
irritability cell का महत्वपूर्ण गुण है , इसी गुण के कारण शरीर में बाह्य उद्दीपनों से excitement उत्पन्न होता है।
5. Reproduction
progeny जीवधारियों का एक विशिष्ट गुण है जो reproduction द्वारा पूर्ण होती है। cell में reproduction का गुण पाया जाता है। cell division द्वारा यह कार्य पूर्ण होता है।
6. Movement
मानव शरीर असख्य cell से मिलकर बना है जिनमें से कुछ cells स्थिर होती है और कुछ सदैव गतिशीलता का गुण दर्शाती है। जैसे - RBC , WBC आदि।
7. Excretion
food के digestion के फलस्वरूप तथा respiration क्रिया एवं अन्य जैविक क्रियाओं के द्वारा शरीर में waste materials का निर्माण होता है जो excretion द्वारा पूर्ण होता है। जैसे - lungs द्वारा respiration क्रिया के दौरान Co2 का बाहर निकलना, skin द्वारा sweat का excretion, kidney द्वारा urine का excretion आदि।
CELL PHYSIOLOGY
Cell Transportation cell का महत्वपूर्ण कार्य है जिसमें cell membrane द्वारा कुछ पदार्थों का cell के आन्तरिक एवं बाहरी भाग में Transportation (आवागमन) होता है। जों cellular transport कहलाता है। cellular transport की क्रिया निम्नलिखित process द्वारा पूर्ण होती है -
1. Passive Transport (निष्क्रिय परिवहन)
a) Simple Diffusion (सामान्य विसरण) b) Facilited Diffusion (सुविधा विसरण)
c) Osmosis (परासरण) 2. Active Transport (सक्रिय परिवहन)
1. Passive Transport
Passive Transport में पदार्थों का गमन cell membrane द्वारा बिना किसी energy की सहायता से high concentration से low concentration की ओर होता है।
(a) Simple Diffusion :- high concentration से low concentration की ओर छोटे एवं lipid में
soluble substances का cell membrane द्वारा गमन Simple Diffusion कहलाता है।
(b) Facilited Diffusion :- यह large molecules के लिए transport की विधि है। जिसमें substances का
गमन protein के माध्यम के साथ होता है अर्थात् प्रोटीन एक वाहक का कार्य करता है।
(c) Osmosis :- अर्द्धपारगम्य झिल्ली द्वारा low concentration वाले solution का high concentration वाले
solution की ओर गमन करना Osmosis कहलाता है।
2. Active Transport
Active Transport के substances का गमन cell membrane द्वारा अतिरिक्त energy की सहायता से होता है।